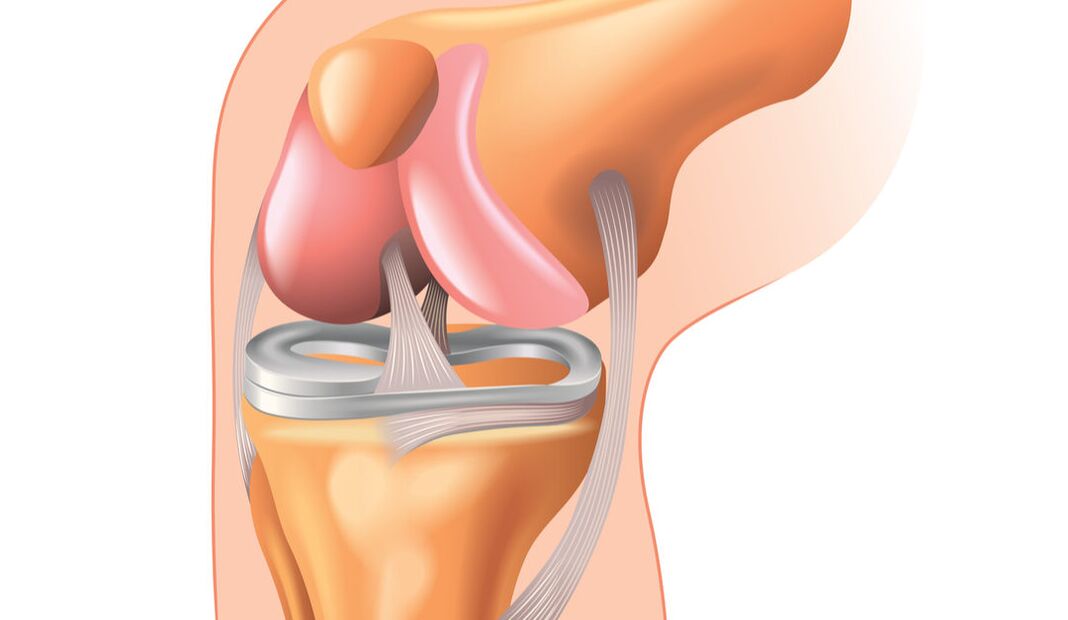
The degenerative inflammatory process in the knee joint, also known as gonorrhea, occurs for many reasons. It has an extremely negative impact on a person's quality of life, sometimes leading to disability. How to treat knee osteoarthritis and prevent complications?
What is arthritis?
About 22% of the world's population has gonorrhea and women are more commonly affected. This devastating disease is characterized by rapid progression.
If treatment is not started promptly, the knee joint can collapse completely. This leads to impaired skeletal muscle function. Movement is possible only with the help of crutches, or the person becomes a hostage in a wheelchair.
The knee joint is the second largest joint after the hip and has the most complex structure. It allows you to bend and straighten your legs in different directions, promoting correct body position and coordination in space. This is a strong and stable joint that can bear a person's weight. Consists of 3 bones: the femur, tibia, and fibula, as well as the kneecap or patella. Includes bone and cartilage structures, muscles, ligaments and nerve fibers.
The disease begins with a violation of blood circulation and nutrition of joint tissues. First of all, the cartilage is affected. The quality and quantity of the synovial fluid that resides in the joint capsule and contributes to the smooth functioning of the knee is reduced. Friction occurs between joint parts. Gradually, the cartilage cracks and collapses. Unprotected bones begin to rub against each other. Pain appears and a crunching sound is heard.
Cause of the disease
It mainly affects older people, especially overweight women. Due to hormonal changes, the cartilage in the knee wears down a lot. Gonorrhea of varying degrees, after 60 years, occurs in more than 80% of people.
There are other reasons for the appearance of knee arthritis:
- congenital joint pathology;
- dysplasia;
- trauma, surgery;
- removal of cartilage or part of it;
- arthritis;
- diseases of the lumbar spine;
- Hormonal disorder;
- low metabolism.
The risk of developing the disease is increased in people who perform repetitive manual labor. This group also includes athletes, people with a sedentary lifestyle and people with unfavorable environmental conditions. Usually the patient is dependent on toxic substances (drugs, alcohol, smoking).
The cause of joint deformity may be work that involves constant hypothermia. The provoking factor is the postmenopausal period, when a woman develops gynecological disorders (fibroadenoma, endometriosis, uterine fibroids). Due to the body's lack of minerals and vitamins, diet may be the cause.
Stages and symptoms
Gonorrhea can be unilateral or bilateral. According to the nature of manifestations, the disease is divided into levels:
- At this stage there are no clear clinical signs. There may be mild discomfort and pain after prolonged exercise that disappears after rest. The pain appears in the morning, when moving, it will go away after a while. Grade 1 arthritis is rarely diagnosed incidentally during a routine examination.
- Pain and stiffness in the knee increases. A person spares his leg and tries to load it less. As a result, the muscles atrophy, the joints are deformed, formations can be felt, and the leg at the knee does not fully extend.
- Constant pain. The legs do not straighten or bend, the patient has difficulty walking. Partial or complete loss of mobility develops. Cartilage is completely destroyed, friction between bones and joints increases with the formation of bone spurs.
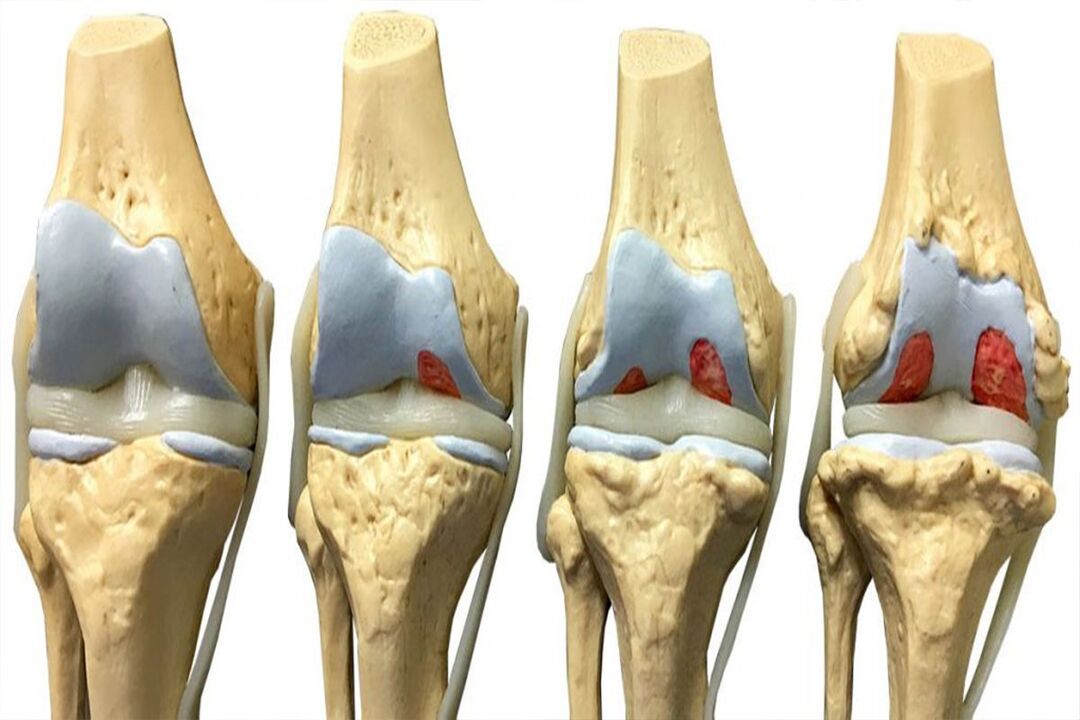
In addition to level 2 and 3 pain, there is also a cracking sound in the knee. Fluid and pieces of cartilage tissue can accumulate in the joint capsule, leading to swelling. In the late stage, the inflammatory process is evident and the knee joint is deformed.
Diagnose
If you have knee pain, you can contact your local doctor who, if necessary, will refer you to an orthopedist, traumatologist, rheumatologist or endocrinologist.
To find the cause and treatment of gonorrhea, a comprehensive diagnosis is needed:
- General blood and biochemical tests;
- rheumatism test;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound and MRI can detect the disease in its early stages;
- arthroscopy.
X-rays can show the condition of the cartilage and bone changes in stages 2 and 3. This is a narrowing of the joint space, bone spurs along the edges of the kneecap, changes in the kneecap. periosteum. Arthroscopy provides more detailed information about the joint cartilage, synovial membrane, and the presence of fluid. This method is also used in knee treatment, to remove pieces of cartilage or meniscus.
Treatment of knee arthritis
Treatment is long and sometimes painful. Appearing once, the disease will remind you for a lifetime. The main drugs used for treatment are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Usually these are drugs based on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from the group of phenylacetic acid derivatives. They eliminate inflammation and pain. The drug is relatively cheap but leads to the formation of ulcers and erosion of the stomach and duodenum. Modern drugs cause fewer side effects but are expensive.
Treatments for stage 1 include preventative measures related to exercise. It is necessary to exercise daily, use contrast showers, swimming pools 2 times a week and prevent increased body weight.
Stage 2 requires immobilization of the joint - using elastic bands, bandages or orthotics. For pain relief, NSAIDs are used as creams and ointments. To reduce the degree of cartilage destruction, patients are prescribed drugs from the chondroprotector group.
Severity requires oral NSAIDs. Indications for intra-articular injection of hormonal drugs - synthetic glucocorticosteroids (GCS), which have high glucocorticosteroids and low mineralocorticosteroid activity. In addition, pain relievers are prescribed.
A hyaluronic acid solution is injected into the joint. It is a substitute for joint fluid and nourishes cartilage. When moving, it acts as a shock absorber for the joints. The operation is painful and is performed by the doctor after the acute stage has subsided. If conservative treatment is unsuccessful, endoscopy will be performed.
Along with drug treatment, exercises using special equipment and simulators (kinesitherapy) are prescribed. Ozone therapy has a positive effect on the condition of the knees. The substance is used externally, administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly, ointments, creams based on ozone. Manipulation stimulates blood circulation, enhances the effects of chondroprotectors and glucocorticosteroids.
Modern dietary supplements are in demand as an alternative to joint rehabilitation drugs. Exercise and massage therapy are indicated. A set of special exercises helps improve blood circulation and nutrition of cartilage cells, increasing the elasticity of ligaments.
Complications and ways to prevent them
Cartilage tissue is destroyed and bones are deformed beyond treatment. In this situation, only surgery will help. There are no ointments or medications that can restore cartilage. Medicines can only stop the process of destroying cartilage tissue.
Gonorrhea progresses gradually, sometimes lasting many years. Without appropriate treatment, the patient's condition will rapidly worsen. The knee cannot function, serious complications appear:
- joint deformity;
- cosmetic defects - curvature of the limb;
- infection of the blood or lymph from another source of the body;
- due to weak ligaments, dislocations and fractures are possible, even when walking normally;
- bony (ankle) fusion occurs in the joint area, making movement impossible.
Complications will develop if the patient does not see a doctor promptly and the disease progresses. Regular preventive examinations and timely treatment of general diseases of the body will help prevent deterioration and maintain the motor function of the limbs.